Password Entropy Explained: Calculate Your Password's True Strength
In an era of sophisticated cyber threats, password strength has never been more critical. But how can you determine if your password is truly secure? Many people rely on simple rules like length or character types, but these can be misleading. A password's real security lies in its unpredictability.
Enter password entropy—the scientific measure that quantifies a password's resistance to brute-force attacks. Understanding this concept is key to creating strong passwords. This guide demystifies the mathematics behind password strength and shows you how to create secure passwords that protect your digital life. With the right approach, generating a strong password is easy, and you can get started now with a tool built on these principles.

Understanding Password Entropy: The Science of Security
Password entropy is a way to measure the randomness or unpredictability of a password. It's calculated in "bits," and the higher the number of bits, the more secure your password is. Think of it like a guessing game. A password with low entropy, like "123456," is easy for a computer to guess. A password with high entropy is incredibly difficult to guess, even for the most powerful supercomputers.
This concept moves beyond simple complexity rules, which often fail to capture true strength. Instead, it provides a mathematical foundation for security. By understanding entropy, you gain a more accurate and reliable way to assess how well your passwords can withstand modern cracking attempts.
Bits, Bytes, and Beyond: The Building Blocks of Entropy
To understand entropy, you first need to understand bits. A "bit" is the smallest unit of data in a computer, representing either a 0 or a 1. Every additional bit of entropy doubles the number of possible combinations a hacker would need to try to guess your password.
For example:
-
A 1-bit password has 2 possibilities (0 or 1).
-
A 2-bit password has 4 possibilities (00, 01, 10, 11).
-
A 10-bit password has 1,024 possibilities (2¹⁰).
-
A 50-bit password has over a quadrillion possibilities (2⁵⁰).
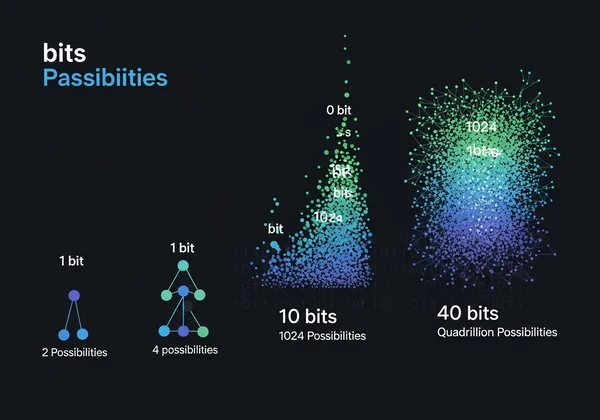
As you can see, even a small increase in entropy bits leads to an exponential increase in security. This is why entropy is the gold standard for measuring password strength—it directly relates to the work required for an attacker to crack it.
Why Password Complexity Can Be Misleading Without Entropy Analysis
Many websites enforce password rules like "must include an uppercase letter, a number, and a symbol." While well-intentioned, these rules can create a false sense of security. A password like "Password1!" might meet these requirements, but it's a common pattern and has relatively low entropy because humans tend to create predictable passwords.
Hackers know these patterns. Their cracking software is designed to try common words, substitutions (like "@" for "a"), and sequential numbers first. A password that seems complex to a human might be one of the first combinations a computer tries. Entropy analysis, on the other hand, measures true randomness, providing a far more accurate assessment of a password's strength against these automated attacks.
The Mathematics of Protection: Calculating Password Entropy
The calculation for password entropy isn't just a random guess; it's based on a clear mathematical formula. Understanding this formula helps you see exactly why certain password creation strategies are more effective than others. It empowers you to make informed decisions about your own digital security.
The core idea measures the size of the character 'pool' and password length. A larger character pool and longer password both contribute to higher entropy, making the result exponentially harder to guess.
Breaking Down the Entropy Formula: H = L × Log₂(N)
The standard formula for calculating password entropy is quite simple: H = L × Log₂(N). Let's break down what each part means:
- H stands for Entropy, the final strength score measured in bits.
- L is the Length of your password (the number of characters).
- N is the Number of possible characters in your character set.
The character set (N) is determined by the types of characters you allow. For example:
- Just lowercase letters (a-z): N = 26
- Lowercase and uppercase letters (a-z, A-Z): N = 52
- Letters and numbers (a-z, A-Z, 0-9): N = 62
- Letters, numbers, and common symbols: N ≈ 94
The Log₂(N) part of the formula calculates how many bits of entropy each character adds. For a password using all 94 characters (letters, numbers, symbols), each character adds about 6.55 bits of entropy (Log₂(94) ≈ 6.55). Therefore, a 12-character password using this set would have an entropy of approximately 78.6 bits (12 × 6.55), which is considered very strong. You can generate a password with this level of strength in seconds.
Entropy in Practice: From Common Passwords to Military-Grade Protection
Let's see how entropy plays out with real-world examples. A common password like "password" uses only 8 lowercase letters. Its entropy is just 37.6 bits (8 × Log₂(26)). A modern computer can crack this instantly.
Now, consider a password generated by a reliable tool. A 16-character random password using uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols has an entropy of about 104 bits (16 × 6.55). Cracking this would take even the most powerful supercomputers trillions of years.
This is the practical difference entropy makes. It transforms your password from a weak lock into a virtually unbreakable digital vault. The goal is to move away from predictable, human-made patterns and embrace the mathematical security of high-entropy, randomly generated credentials.
How PasswordGenerator.vip Implements Entropy Analysis
At PasswordGenerator.vip, we don't just give you a random string of characters; we provide a tool engineered for true security. Our generator is built on the principles of password entropy. Every password you create is instantly analyzed and graded, giving you immediate feedback on its real-world strength.
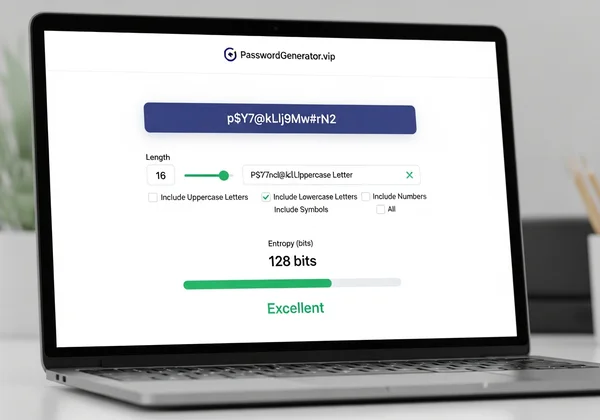
Our commitment to security is twofold. First, we use robust entropy calculations to ensure the passwords themselves are strong. Second, we protect your privacy. All passwords are generated directly in your browser on your device. We never see, store, or transmit your passwords, guaranteeing that your new, high-entropy password remains yours and yours alone. You can try our free tool to see this process in action.
Our Entropy Thresholds: What "Weak," "Medium," and "Strong" Really Mean
Our tool labels passwords as 'Weak,' 'Medium,' 'Strong,' or 'Excellent' based on calculated entropy. Here's what these labels mean for your security:
- Weak (under 40 bits): Highly vulnerable. Can be cracked in seconds or minutes. These are often short, common, or predictable passwords.
- Medium (40-60 bits): Better, but still at risk from dedicated attackers. May resist casual attempts but will fall to sustained brute-force attacks.
- Strong (60-100 bits): A good target for most online accounts. These passwords would take years or centuries to crack with current technology.
- Excellent (100+ bits): Considered computationally infeasible to crack. Ideal for critical accounts like email, banking, and password managers.
Our tool gives you this real-time feedback so you can adjust the length and character sets to meet the security level you need.
Maximizing Entropy: Our Random Generation Process Explained
To create a password with the highest possible entropy, you need true randomness. Humans are terrible at creating random patterns, so we rely on a cryptographically secure pseudo-random number generator (CSPRNG). This is a sophisticated algorithm built into modern web browsers that produces values that are, for all practical purposes, unpredictable.
When you click "Generate" on PasswordGenerator.vip, our code asks the browser's CSPRNG for a series of random numbers. We then map these numbers to the character set you selected (e.g., uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols). This ensures that every character in your new password is chosen with equal and independent probability. This process, performed entirely on your device, maximizes entropy and creates a password that is truly resistant to guessing.
Industry Standards: NIST Guidelines and Entropy Requirements
When it comes to digital identity and security, few organizations are more respected than the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Their publications provide a benchmark for governments and industries worldwide, including recommendations on password strength and entropy.
Aligning with these expert guidelines is crucial for any trustworthy security tool. It demonstrates a commitment to proven best practices rather than arbitrary rules. At PasswordGenerator.vip, our approach is heavily influenced by these authoritative standards, ensuring the advice and tools we provide are grounded in expert consensus.
NIST SP 800-63B: What the Experts Recommend for Entropy
NIST's Special Publication 800-63B offers detailed guidance on digital identity, including password policies. A key takeaway is its shift away from mandatory complexity rules (like requiring symbols) and toward an emphasis on length and checking against breached password lists.
NIST recognizes entropy as the core measure of strength. While they don't mandate a single entropy value for all use cases, the principles suggest that user-chosen passwords should have a minimum level of entropy, and randomly generated passwords should be significantly stronger. Modern security practices often aim for at least 70-80 bits of entropy for strong protection, a level easily achieved with a custom password generator.
Entropy vs. Usability: Finding the Security Sweet Spot
A 50-character password with 300+ bits of entropy is incredibly secure, but it's also impossible to remember. This highlights the classic trade-off between security and usability. The perfect password is one that is strong enough for its purpose but practical enough for you to manage.
This is where different password generation modes become useful:
- Random Passwords: For use with a password manager, where memorization isn't needed. You can maximize entropy with long, complex strings.
- Memorable Passphrases: For master passwords or situations where you need to type it from memory. A passphrase like
Correct-Horse-Battery-Stapleuses four random words to achieve high entropy while remaining memorable. Our "Memorable" option is designed for exactly this purpose.
The key is to find the right balance for your needs, and a versatile tool gives you the options to do so securely.
Upgrade Your Password Security with Entropy-Driven Protection
Now that you understand password entropy, you're no longer guessing about security—you're making informed decisions. Think of it as upgrading from a flimsy lock to a fortified vault for your digital life. When you focus on entropy, your passwords become mathematically sound defenses against modern threats.
What you should remember:
- Entropy is the true measure of password strength, quantifying its randomness and resistance to attacks.
- Length and a large character set are the two primary drivers of high entropy.
- Rely on tools that use secure random generation, as humans are not good at creating unpredictable patterns.
Are you ready to stop wondering if your passwords are secure and start creating ones that are? Use a tool built on the science of entropy. Visit PasswordGenerator.vip to create a strong, high-entropy password for your most important accounts in seconds.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is password entropy different from password strength?
Password strength is a general term, while password entropy is the specific, measurable calculation of that strength. Think of it this way: "strength" is the goal, and "entropy" is the scientific metric used to prove you've reached it. A password's entropy value in bits gives you a precise understanding of how hard it would be to crack.
What entropy level should my password have for different types of accounts?
For low-risk accounts, an entropy of 40-60 bits might be acceptable. For important accounts like your primary email, social media, or online banking, you should aim for at least 70-80 bits of entropy. For critical data, like a master password for a password manager, aiming for 100+ bits is the best practice.
Can a longer, simpler password have higher entropy than a shorter, complex one?
Absolutely. This is a core insight from entropy analysis. For example, a 20-character password using only lowercase letters has an entropy of about 94 bits (20 × 4.7). A 10-character password using all character types has only 65 bits (10 × 6.5). This is why length is often considered the single most important factor in password strength.
How does PasswordGenerator.vip calculate entropy values for your passwords?
Our tool uses the standard formula: H = L × Log₂(N). When you adjust the password length (L) and select character types (which determines N), we instantly recalculate the entropy (H) in the background. This allows our strength meter to give you real-time, accurate feedback on your password's security level, helping you create a password that meets your needs.
Are there minimum entropy requirements recommended by security experts?
Yes, while there isn't one universal number, many experts, referencing guidelines like those from NIST, recommend a minimum of around 70-80 bits of entropy for passwords protecting sensitive data. To achieve this easily and securely, we recommend using a trusted tool. You can create a secure password that meets these expert recommendations on our site.